Rustc Arch - 0
转眼已经在 Rustc 的官方 Zuilp 群, 待了快三个月了。之前向 Rustc 提交的 pr 居然一直没过, 后来才知道被别人改掉了。倒是, 在其他的地方( 比如 rust-lang/this-week-in-rust 和 Clippy 上帮忙 review了代码)也算是做出了微小的贡献吧。不过, Rust 社区还是很友好的, 会帮助其他愿意开发的志愿者, 给初学者分配 mentor (可是 我一直没被分到)。我自己也看了几章官方的开发手册, 算是有一些经验吧。下面我会介绍一下 rustc 的 Working groups, 并且简单总结一下 rustc 的整体架构, 希望能给其他感兴趣的人做一个参考。
Working groups
Intro
编译器团队正在进行的大部分工作和计划都是由工作组 (Work)执行的。为新加入的贡献者分配任务, 所有任务都集中在一个领域,并有指定的 metor 。
详细的表格在这里
| Name | Status | Short Description | Zulip Stream |
|---|---|---|---|
| Async-await Implementation | Active | Implementing async-await | #t-compiler/wg-async-await |
| Diagnostics | Active | Use crates.io crates for diagnostics rendering and make emitting diagnostics nicer. | #t-compiler/wg-diagnostics |
| Rustc Dev Guide | Active | Make the compiler easier to learn by ensuring that rustc-dev-guide is “complete” | #t-compiler/wg-rustc-dev-guide |
| LLVM | Incubating | Working with LLVM upstream to represent Rust in its development | #t-compiler/wg-llvm |
| Meta | Paused | How compiler team organizes itself | #t-compiler/wg-meta |
| MIR Optimizations | Active | Write MIR optimizations and refactor the MIR to be more optimizable. | #t-compiler/wg-mir-opt |
| Non-Lexical Lifetimes (NLL) | Retired | Implementing non-lexical lifetimes | #t-compiler/wg-nll |
| Parallel-rustc | Paused | Making parallel compilation the default for rustc | #t-compiler/wg-parallel-rustc |
| Polonius | Active | Exploring the integration of the “NLL 2.0”-like “Polonius analysis” into rustc | #t-compiler/wg-polonius |
| Polymorphization | Active | Implement an analysis to detect when functions can remain polymorphic during code generation. | #t-compiler/wg-polymorphization |
| Prioritization | Active | Triaging bugs, mainly deciding if bugs are critical (potential release blockers) or not. | #t-compiler/wg-prioritization |
| Profile-Guided Optimization | Retired | Implementing profile-guided optimization for rustc | #t-compiler/wg-profile-guided-optimization |
| RFC 2229 | Active | Make a closure capture individual fields of the variable rather than the entire composite variable | #t-compiler/wg-rfc-2229 |
| RLS 2.0 | Active | Experimenting with a new compiler architecture tailored for IDEs | #t-compiler/wg-rls2.0 |
| Rustc pipelining | Retired | Enable Cargo to invoke rustc in a pipelined fashion, speeding up crate graph compiles. | #t-compiler/wg-pipelining |
| Self-Profile | Active | Improving the -Z self-profile feature |
#t-compiler/wg-self-profile |
| Traits | Active | Improving the trait-system design + implementation | #t-compiler/wg-traits |
ps 现在 RLS 重构了 和 RA 有竞争关系. 我也看了 RA 的整体架构, 之后会总结一篇文章。
我现在算是 Diagnostics的成员, 主要还是帮助完成测试样例 ,以及完成更好的报错信息。
How can I get involved?
那么如何加入这个 workgroups 呢?
其实很简单, 你只需要下载一个 Zuilp 就好了。之后加入他们的群组, 找到你喜欢的组, 然后自我介绍一下。会有人给你分派任务, 你也可以自己逛一下 Rust 的其他仓库,找到有 Help_wanted字样的 issue , 说明自己想参与开发就可以了。
就算是没时间参与 / 提交的代码没有被采纳, 也可以跟进他们的会议 , 和大家一起讨论问题, 一起进行 issue 的商讨。
想更深入的理解 rustc 并且参与到 rust 的开发中来的话, 建议阅读一下 官方的 rustc-dev-guide。
Rustc 的架构 (非常粗略)
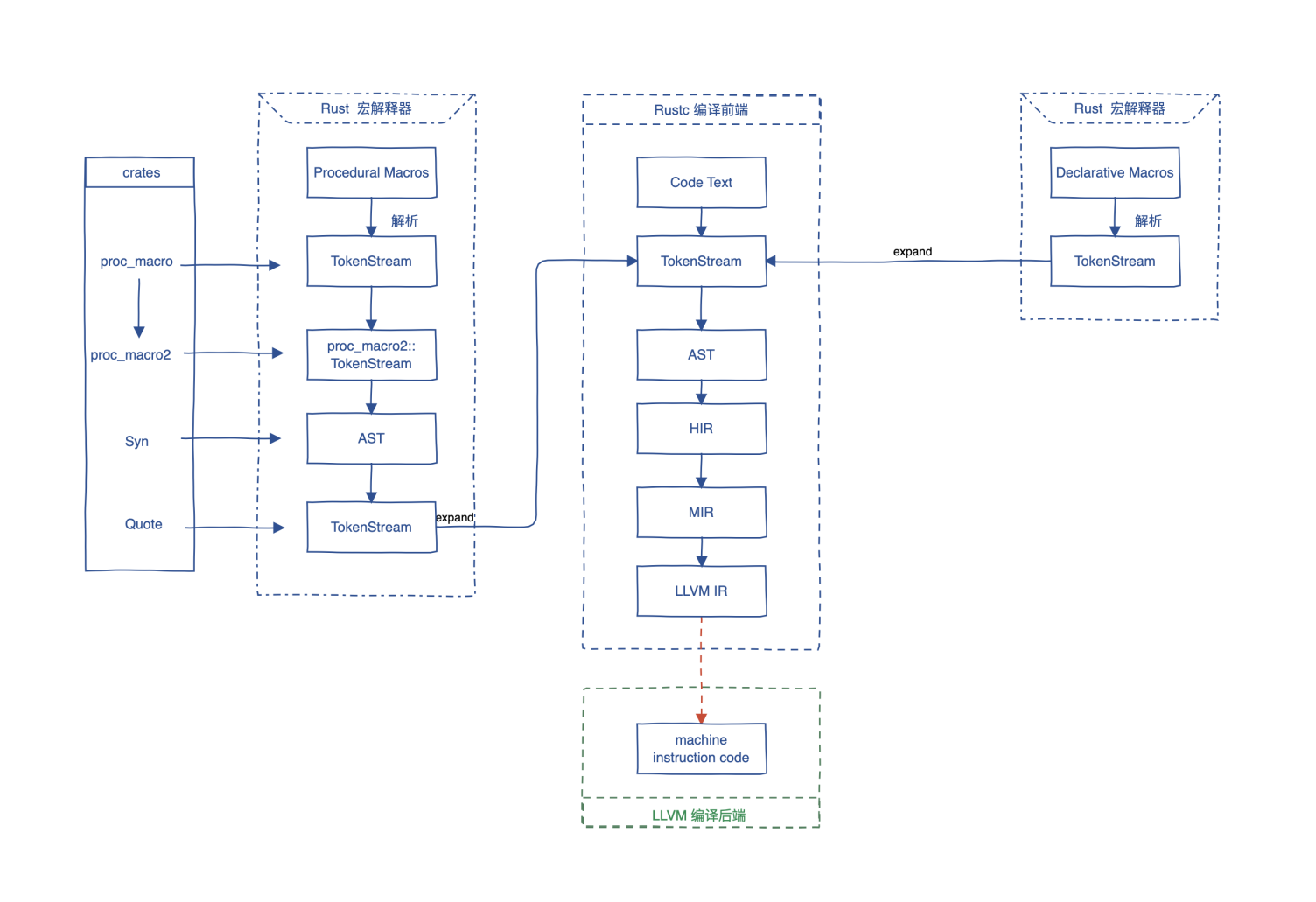
来源: rust_magazine_2021
rust的编译器在两方面独具特色:首先它会对你的代码进行别的编译器不会进行的操作(比如借用检查),并且有许多非常规的实现选择(比如查询)。
Rustc 编译流程
-
编译步骤从用户编写 Rust 程序文本并且使用
rustc编译器对其进行处理开始。命令行参数指明了编译器需要做的工作。 举个例子,我们可以启用开发版特性(-Z标识),执行check——仅执行构建,或者得到 LLVM-IR 而不是可执行机器码。 通过使用cargo,rustc的执行可能是不直接的。 -
命令行参数解析在
rustc_driver中发生。这个 crate 定义了用户请求的编译配置 并且将其作为一个rustc_interface::Config传给接下来的编译过程。fn arg_expand(arg: String) -> Result<Vec<String>, Error> { if let Some(path) = arg.strip_prefix('@') { let file = match fs::read_to_string(path) { Ok(file) => file, Err(ref err) if err.kind() == io::ErrorKind::InvalidData => { return Err(Error::Utf8Error(Some(path.to_string()))); } Err(err) => return Err(Error::IOError(path.to_string(), err)), }; Ok(file.lines().map(ToString::to_string).collect()) } else { Ok(vec![arg]) } } pub fn arg_expand_all(at_args: &[String]) -> Vec<String> { let mut args = Vec::new(); for arg in at_args { match arg_expand(arg.clone()) { Ok(arg) => args.extend(arg), Err(err) => rustc_session::early_error( rustc_session::config::ErrorOutputType::default(), &format!("Failed to load argument file: {}", err), ), } } args } rustc_driver 的部分代码 -
原始的 Rust 源文本被位于
rustc_lexer的底层词法分析器分析。在这个阶段,源文本被转化成被称为 tokens 的 子源码单位序列。 词法分析器支持 Unicode 字符编码( 汉 语 编 程)。 -
token 序列传给了位于
rustc_parse的高层词法分析器以为编译流程的下一个阶段做准备。StringReader结构体在这个阶段被用于执行一系列的验证工作并且将字符串转化为驻留符号(稍后便会讨论 驻留)。 [字符串驻留] 是一种将多个相同的不可变字符串只存储一次的技术。 -
词法分析器有小的接口并且不直接依赖于
rustc中的诊断基础设施。反之,它提供在rustc_parse::lexer::mod中被发送为真实诊断 的作为普通数据的诊断。 -
解析器 将从词法分析器中得到的token序列转化为抽象语法树(AST)。它使用递归下降(自上而下)的方式来进行语法解析。 解析器的 crate 入为
rustc_parse::parser::item中的Parser::parse_crate_mod()以及Parser::parse_mod()函数。 外部模块解析入口为rustc_expand::module::parse_external_mod。 以及宏解析入口为Parser::parse_nonterminal()。 -
解析经由一系列
Parser工具函数执行,包括fn bump,fn check,fn eat,fn expect,fn look_ahead。 -
解析是由要被解析的语义构造所组织的。分离的
parse_*方法可以在rustc_parseparser文件夹中找到。 源文件的名字和构造名相同。pub mod attr; mod attr_wrapper; mod diagnostics; mod expr; mod generics; mod item; mod nonterminal; mod pat; mod path; mod stmt; mod ty; -
这种命名方案被广泛地应用于编译器的各个阶段。你会发现有文件或者文件夹在解析、降低、类型检查、HIR降低、以及MIR源构建。
-
宏展开、AST验证、命名解析、以及程序错误检查都在编译过程的这个阶段进行。
-
解析器使用标准
DiagnosticBuilderAPI 来进行错误处理,但是我们希望在一个错误发生时, 尝试恢复、解析Rust语法的一个超集。 -
rustc_ast::ast::{Crate, Mod, Expr, Pat, ...}AST节点从解析器中被返回。 -
我们接下来拿到AST并且将其转化为高级中间标识(HIR)。这是一种编译器友好的 AST 示方法。 这包括到很多如循环、
async fn之类的解糖化的东西。 -
我们使用 HIR 来进行[类型推导]。 这是对于一个表达式,自动检测其类型的过程。
-
HIR之后 被降低为中级中间标识(MIR)。
- 同时,我们构造 THIR ,THIR是更解糖化的 HIR。THIR被用于模式和详尽性检验。 同时,它相较于 HIR 更容易被转化为MIR。
-
MIR被用于[借用检查]。
-
在 MIR 上做许多优化 它仍然是通用的, 并且这样能改进我们接下来生成的代码,同时也能加快编译速度。
- MIR 是高级(并且通用的)表示形式,所以在 MIR 层做优化要相较于在 LLVM-IR 层更容易。 举个例子,LLVM看起来是无法优化
simplify_try这样的模式,而mir优化则可以。
- MIR 是高级(并且通用的)表示形式,所以在 MIR 层做优化要相较于在 LLVM-IR 层更容易。 举个例子,LLVM看起来是无法优化
-
Rust 代码是 单态化 SSA 的,这意味着对于所有所有通用代码进行带被具体类型替换的类型参数的拷贝。 要做到这一点,我们要生成一个列表来存储需要为什么具体类型生成代码。这被称为 单态集合。
-
codegen。
- 代码生成(codegen)是将高等级源表示转化为可执行二进制的过程。
rustc使用LLVM来进行代码生成。第一步就是将 MIR 转化为 LLVM 中间表示(LLVM IR)。 这是 MIR 依据我们由上一步生成的列表来真正被单态化的时候。 - LLVM IR 被传给 LLVM,并且由其进行更多的优化。之后它产生机器码, 这基本就是添加了附加底层类型以及注解的汇编代码。(比如一个 ELF 对象或者 wasm)。
- 不同的库/二进制内容被链接以产生最终的二进制内容。
- 最新版本的 codegen 实际上支持多种后端 。rustc_codegen_cranelift, rustc_codegen_llvm , rustc_codegen_ssa。