内存管理内幕(2) –fastbin
已经好久都没有更新博客了,今天准备写一篇关于malloc的学习笔记
前言
上篇文章中, 详细介绍了malloc的基本实现。但是在glibc malloc中,我们用的是一种完全不一样的策略来完成chunk的管理。

基础知识
bin介绍
bin是一种记录free chunk的链表 其中有四种不同的类型 1.Fast bin 2.Unsorted bin=bin 1= 3.Small bin =bin 2-63= 4.Large bin =bin 64-126=
struct malloc_state
{
……
/* Fastbins */
mfastbinptr fastbinsY[NFASTBINS];
……
/* Normal bins packed as described above */
mchunkptr bins[NBINS * 2 - 2]; // #define NBINS 128
……
};
其中的$fastbin$是保存地址的数组 一共有126个bin
struct malloc_chunk {
/* #define INTERNAL_SIZE_T size_t */
INTERNAL_SIZE_T prev_size; /* Size of previous chunk (if free). */
INTERNAL_SIZE_T size; /* Size in bytes, including overhead. */
struct malloc_chunk* fd; /* 这两个指针只在free chunk中存在*/
struct malloc_chunk* bk;
/* Only used for large blocks: pointer to next larger size. */
struct malloc_chunk* fd_nextsize; /* double links -- used only if free. */
struct malloc_chunk* bk_nextsize;
};
fd 和 bk 的分别指向 for/backword的数据结构
再源码中我们还可以看见
1659 /* Fastbins */
1660 mfastbinptr fastbinsY[NFASTBINS];
这个地方的fastbinY是用来保存fastbin的数组,fastbin是根据长度存放数组的,所以index=1存放的是48,2->64, 3->80, 4->96, 5->112, 6->128, 7->144, 8->160,
fastbin
引用自在这里
M_MXFAST (since glibc 2.3) Set the upper limit for memory allocation requests that are satisfied using "fastbins". (The measurement unit for this parameter is bytes.) Fastbins are storage areas that hold deallocated blocks of memory of the same size without merging adjacent free blocks. Subsequent reallocation of blocks of the same size can be handled very quickly by allocating from the fastbin, although memory fragmentation and the overall memory footprint of the program can increase. The default value for this parameter is 64*sizeof(size_t)/4 (i.e., 64 on 32-bit architectures). The range for this parameter is 0 to 80*sizeof(size_t)/4. Setting M_MXFAST to 0 disables the use of fastbins.
特性
1)chunk size,那就表示该malloc_chunk的实际整体大小。
2)chunk unused size,该malloc_chunk中刨除诸如prev_size,size,fd和bk可用的大小。因此,对free chunk而言,可用大小比实际整体大小少16字节。
在内存分配和释放过程中,fast bin是所有bin中操作速度最快的。下面详细介绍fast bin的一些特性:
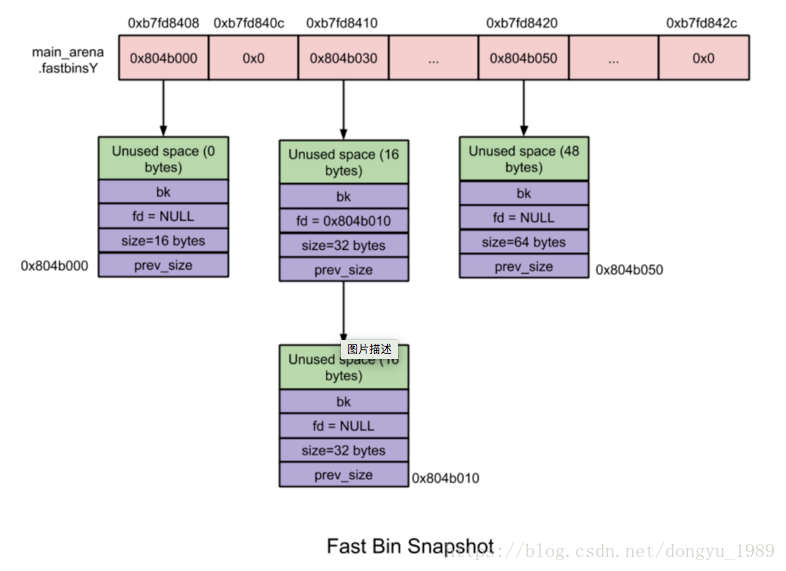
2)每个fast bin都是一个单链表(只使用fd指针)。为什么使用单链表呢?因为fast bin中无论是添加还是移除fast chunk,都是对“链表尾”进行操作,而不会对中间的fast chunk进行操作。更具体点就是LIFO(后入)算法:添加操作(free内存)就是将新的fast chunk加入链表尾,删除操作(malloc内存)就是将链表尾部的fast chunk删除。需要注意的是,为了实现LIFO算法,fashbinsY数组中每个fastbin元素均指向了该链表的rear end(尾节点),而尾结点通过其fd指针指向前一个结点,以此类推。
3)chunk size:10个fast bin中所包含fast chunk size是按照步进8字节排列,即第一个fast bin中所有fast chunk size均为16字节,第二个fast bin为24字节,以此类推。在进行malloc初始化的时候,最大的fast chunk size被设置为80字节(chunk unused size 为64字节),因此模式情况下大小为16到80字节的chunk被分配到fast chunk。
4)不会对free chunk进行合并操作。鉴于设计fast bin的初衷就是进行快速的小内存分配和释放,因此系统将fast bin的chunk的P总是设置成1,这样即使当fast bin中某个chunk同一个free chunk相邻的时候,系统也不会进行自动合并操作
5)初始化的时候fast bin支持的最大内存大小以及所有fast bin链表都是空的,所以当最开始使用malloc申请内存的时候,即使申请的内存大小属于fast chunk的内存大小,它也不会交由fast bin来处理,而是向下传递交由small bin来处理,如果small bin也为空就交给unsorted bin处理。
再free掉chunk之后,就会被放到相印的fastbin中。
结构
gdb-peda$ heap
Arena(s) found:
arena @ 0x7ffff7dd1b20
gdb-peda$ fastbins
[!] No gdb frame is currently selected.
fastbins
[ fb 0 ] 0x7ffff7dd1b28 -> [ 0x0 ]
[ fb 1 ] 0x7ffff7dd1b30 -> [ 0x0 ]
[ fb 2 ] 0x7ffff7dd1b38 -> [ 0x0 ]
[ fb 3 ] 0x7ffff7dd1b40 -> [ 0x0 ]
[ fb 4 ] 0x7ffff7dd1b48 -> [ 0x0 ]
[ fb 5 ] 0x7ffff7dd1b50 -> [ 0x0 ]
[ fb 6 ] 0x7ffff7dd1b58 -> [ 0x0 ]
[ fb 7 ] 0x7ffff7dd1b60 -> [ 0x0 ]
[ fb 8 ] 0x7ffff7dd1b68 -> [ 0x0 ]
[ fb 9 ] 0x7ffff7dd1b70 -> [ 0x0 ]
其中的$arena$是各种bin的首链表
接着来看chunk的结构
1040 struct malloc_chunk {
1041
1042 INTERNAL_SIZE_T mchunk_prev_size; /* Size of previous chunk (if free). */
1043 INTERNAL_SIZE_T mchunk_size; /* Size in bytes, including overhead. */
1044
1045 struct malloc_chunk* fd; /* double links -- used only if free. */
1046 struct malloc_chunk* bk;
1047
1048 /* Only used for large blocks: pointer to next larger size. */
1049 struct malloc_chunk* fd_nextsize; /* double links -- used only if free. */
1050 struct malloc_chunk* bk_nextsize;
1051 };
......
1068 An allocated chunk looks like this:
1069
1070
1071 chunk-> +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
1072 | Size of previous chunk, if unallocated (P clear) |
1073 +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
1074 | Size of chunk, in bytes |A|M|P|
1075 mem-> +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
1076 | User data starts here... .
1077 . .
1078 . (malloc_usable_size() bytes) .
1079 . |
1080 nextchunk-> +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
1081 | (size of chunk, but used for application data) |
1082 +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
1083 | Size of next chunk, in bytes |A|0|1|
1084 +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
......
1094 Free chunks are stored in circular doubly-linked lists, and look like this:
1095
1096 chunk-> +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
1097 | Size of previous chunk, if unallocated (P clear) |
1098 +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
1099 `head:' | Size of chunk, in bytes |A|0|P|
1100 mem-> +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
1101 | Forward pointer to next chunk in list |
1102 +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
1103 | Back pointer to previous chunk in list |
1104 +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
1105 | Unused space (may be 0 bytes long) .
1106 . .
1107 . |
1108 nextchunk-> +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
1109 `foot:' | Size of chunk, in bytes |
1110 +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
1111 | Size of next chunk, in bytes |A|0|0|
1112 +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
其中可以看到size字段 的, 后三个字段是用来作为标志位的。表示上一个chunk是否在使用中,不过在fast chunk/bin中P标志位永远是1,free操作并不会修改fastbin的标志位,所以pre_size,前一个不在使用中的chunk的大小,因为P=1。 chunk总是16的倍数,在malloc小于16byte的数时, 我们可以获得chunk的最小大小为32byte。
参考链接
内存管理学习一直会更新的